The Female Reproductive Anatomy
Many girls and teens wonder about their reproductive organs and whether they are normal.
The information below provides the name for each body part and its specific function, along with a diagram to show where it is located on the female body.
Learn your reproductive anatomy
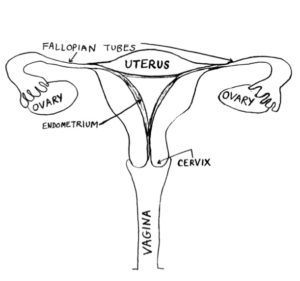
Internal organs (inside the body)
- Vagina: The passageway between the outside of the female body and the uterus.
- Cervix: Located at the top of the vagina, this is the lower most part of the uterus.
- Uterus: A pear-shaped organ. It is made of muscle and can stretch and grow when a woman becomes pregnant. The uterus has a special, inner lining called the endometrium which can shed each month during the menstrual cycle, or where a fertilized egg can implant when pregnancy occurs.
- Fallopian Tubes: The passageway that goes from the uterus to very close to each ovary. When an egg is released from the ovary the ends of the fallopian tube sweep up the egg so it can go to the uterus. There is a tube from each ovary to the uterus.
-
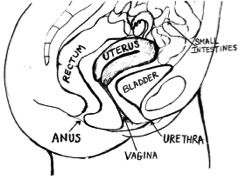
Female reproductive anatomy – internal side view Ovaries: The organs that make and holds the female cells necessary for human reproduction (also called eggs). There is an ovary on each side of the uterus. Each ovary is about the size of a large strawberry. The ovaries produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which play an important part during the changes of puberty, the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
- Bladder: Part of the urinary system that holds urine (pee). It is located in front of the uterus.
- Rectum: Part of the gastrointestinal system that holds feces (poop). It is located behind the uterus and vagina.
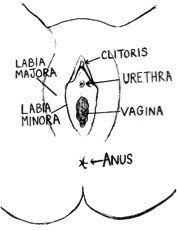
External organs (outside the body)
- Vulva: The entire area of the soft skin between a female’s legs. The vulva includes the labia, the vaginal opening, the clitoris, etc. The vulva is also called the female genitals.
- Labia: These are the soft folds of skin on the vulva. The labia majora are the thicker, outer folds. This skin will grow pubic hair as a girl gets older. The labia minora are thinner, inner folds and surround the urethra and the vaginal opening.
- Clitoris: Small, sensitive area of skin on the vulva.
- Urethra: The small opening where urine leaves the body.
- Vaginal opening: The lower opening of the vagina (the passageway to the uterus).
- Anus: The lower opening of the gastrointestinal system; not part of the genitals. This is connected to the rectum.
